What is Algorithmic Alert Correlation?
The IT Operations tool stack is becoming exponentially more complex. This requires the utilization of a breadth of diverse monitoring tools in order to quickly detect and ultimately resolve critical issues before they can inflict real damage on the business.
Most large enterprises already have a host of preferred monitoring tools installed and working. It doesn’t take long for the alert volume being generated from all these different tools to become overbearing. The term “alert fatigue” applies to the frustration NOC operators experience trying to manually sort through and triage all of these individual events. Alert floods cause distraction and cost valuable time that could be better spent remediating actual root cause.
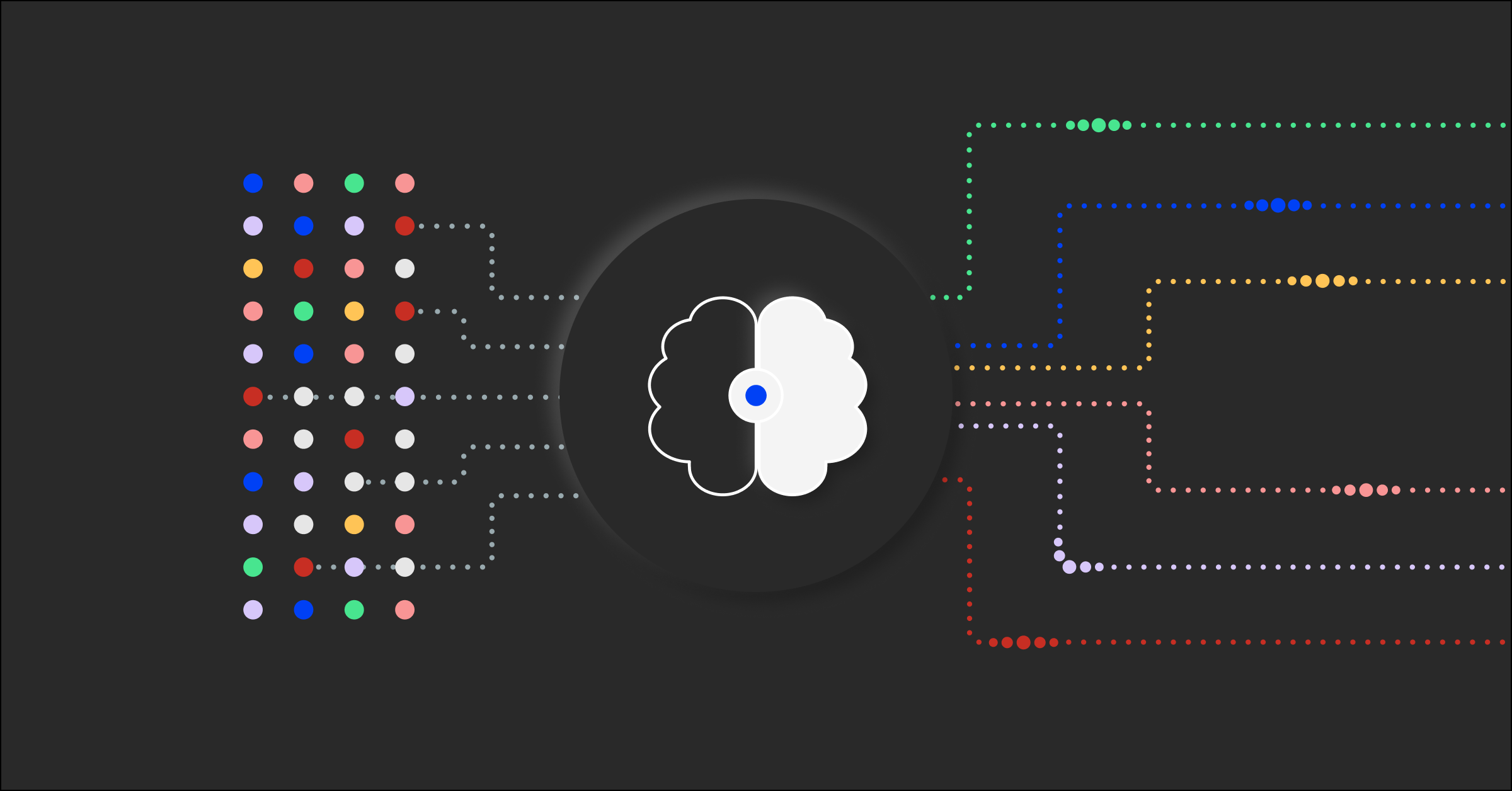
Algorithmic alert correlation is an intelligent way to make sense out of this deluge of machine data and separate the signal from the noise. It quickly identifies patterns in a fully customizable manner to isolate critical issues. Algorithmic alert correlation can also be automated and create system-generated patterns through machine learning.
How does Algorithmic Alert Correlation work?
BigPanda ingests the raw alert data via open integrations with best-of-breed ITOM monitoring systems – including AppDynamics, Nagios, Splunk and many more. The data is normalized into a common and more easily digestible format. Further enrichment of the data can be performed via configuration information, operational categories and other custom tags.
Then BigPanda’s Algorithmic Alert Correlation patterns kick in to automatically find associations amongst the alerts. Alerts are intelligently clustered into high-level actionable groupings called Incidents. When performing the clustering, the patterns can look against and evaluate the following properties:
- Topology: the host, host group, service, application, cloud or other infrastructure element that emits the alerts. Alerts are more likely to be related when they come from the same infrastructure area.
- Time: the rate at which related alerts occur. Alerts occurring around the same time are more likely to be related than alerts occurring far apart.
- Context: the type of alerts. Some alert types imply a relationship between them, while others do not.
BigPanda evaluates all matching patterns in real time, as soon as alerts are received, and determines whether to update an existing incident or create a new one.
Correlation patterns are the driving force behind how exactly alerts get clustered by BigPanda into incidents. To increase the effectiveness of alert correlation, correlation pattern definitions can be customized based on the structure and processes of the customer’s production infrastructure. For example, created patterns can correlate:
- Network-related connectivity issues within the same data center
- Application-specific checks on the same host
- Load-related alerts from multiple servers in the same database cluster
- Low memory alerts on a distributed cache
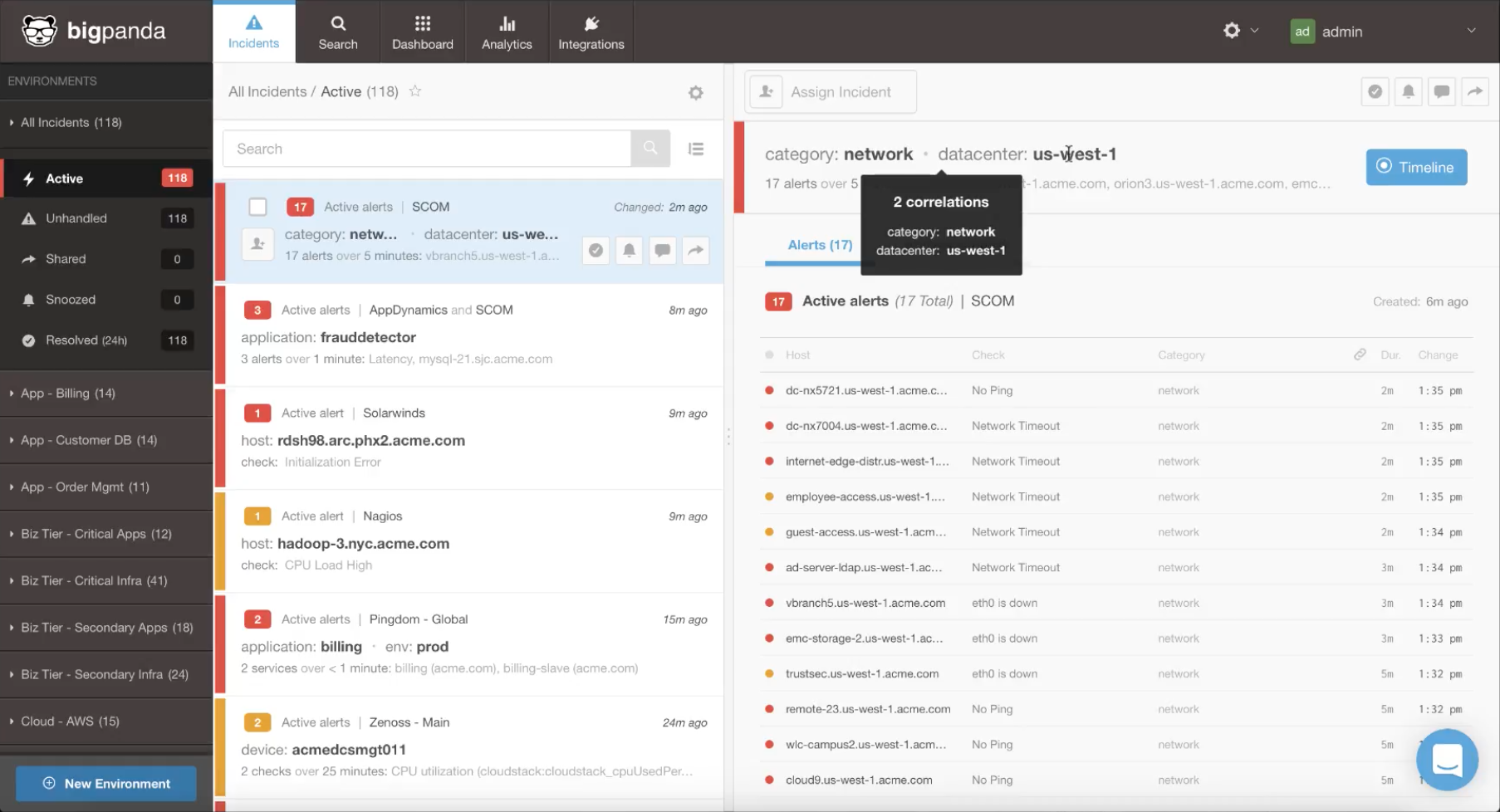
BigPanda is completely open and interoperable, meaning it was designed to protect past technology investments and correlate alerts from whatever monitoring data is available. We can correlate event data from a host of sources including systems, applications, logs, networks, even synthetic sources such as KeyNote. Out-of-the-box integration is supported on a wide range of popular tools, from AppDynamics to Splunk to Solarwinds. For custom integrations, BigPanda offers a REST API for our alerting features that can easily be adapted to any environment. There is literally no monitoring data we can’t reach, whether from legacy or cloud, on-premise or distributed apps and infrastructure.
In part two of this series, we look at how BigPanda allows IT operations personnel to edit and configure the alert correlation patterns to their unique environment.
To dig deeper, check out the following posts: