Five core incident response phases for ITOps
What are the five core incident response phases?
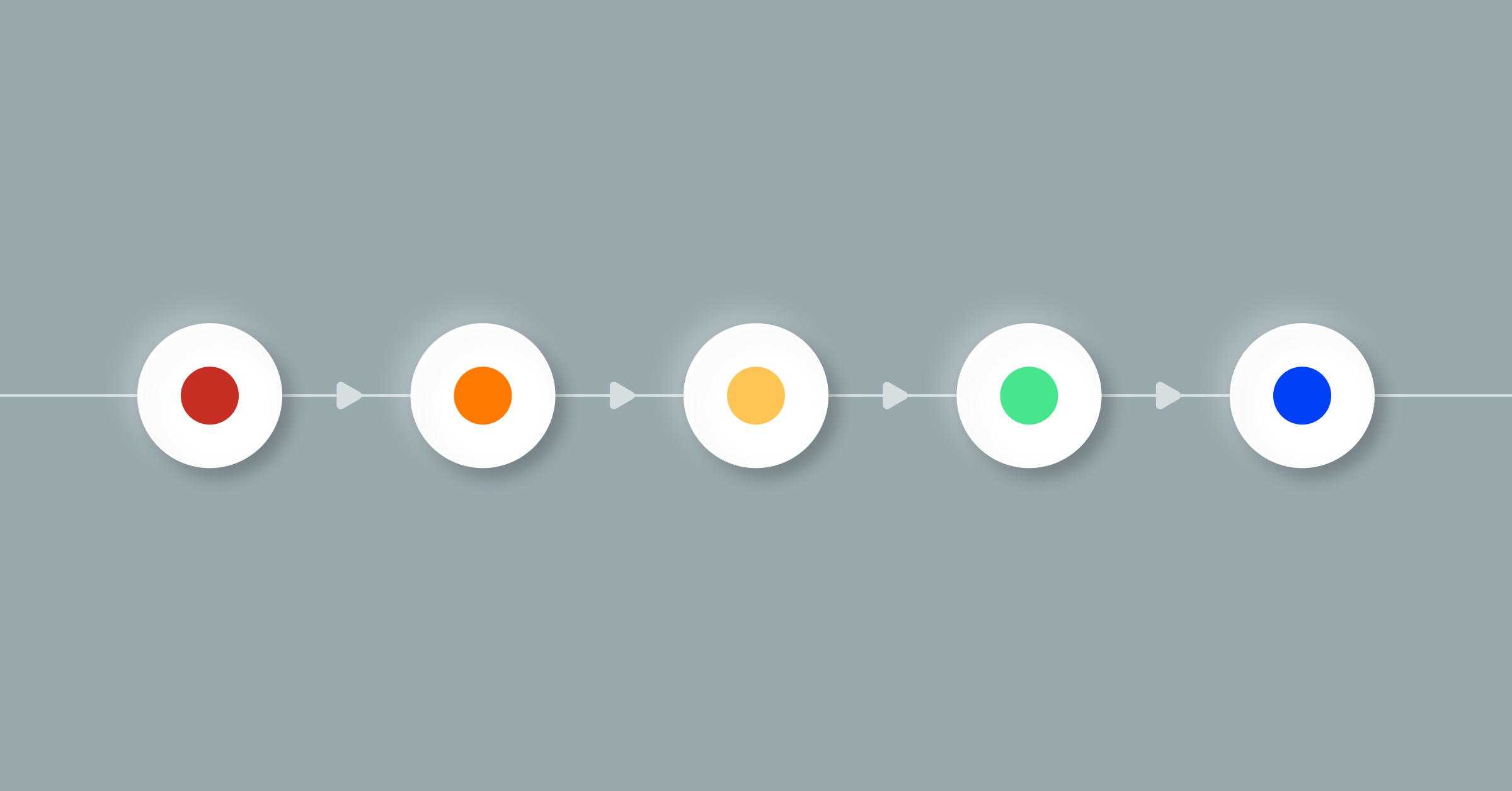
Effective IT event management is about more than restoring services. Managing and mitigating threats involves a comprehensive approach with five incident response phases:
- Identification
- Categorization
- Prioritization
- Response and resolution
- Closure
It’s crucial to take a structured approach to addressing disruptive events. Incident response involves multiple phases to minimize the impact and prevent service outages.
An “incident” is any event that disrupts normal operations or threatens your information systems. Think of system outages, hardware failures, or natural disasters. The goal of incident response, particularly as outlined in the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) framework, is twofold:
- Promptly restore regular service operation. Bring affected services back online quickly so you can resume normal business activities with minimal downtime and disruption.
- Minimize adverse impact on business operations. Mitigate damage, preserve critical data, and ensure the incident does not escalate further.
Phase 1. Identification
Continuous IT infrastructure monitoring is crucial to detect unusual activities or anomalies that could indicate a system or security incident. This phase sets the stage for all subsequent actions, allowing for prompt and effective response. Key activities of incident identification include:
- Monitor and analyze logs and alerts from various devices and systems.
- Identify deviations from normal network behavior.
- Employ real-time automated incident detection and response tools to spot potential threats in real time.
Phase 2: Categorization
Categorization helps define the nature and scope of the incident, which are essential for identifying the appropriate response strategy. Categories generally include hardware failures, software failures, data breaches, and system outages. Categorization activities include:
- Analyze the incident’s characteristics to determine its type.
- Assess the affected systems and potential impact on business operations.
- Document the incident’s specifics for accurate classification.
Phase 3: Prioritization
Not all incidents are created equal. Assess the severity and potential impact of the incident based on factors such as the sensitivity of the affected data, the number of users impacted, and the criticality of the affected systems. Address high-priority incidents that pose significant risks to critical business functions immediately to neutralize the most damaging threats. Key activities for prioritization include:
- Evaluate the incident’s potential to disrupt business operations.
- Assess the urgency and possible consequences of the incident.
- Prioritize incidents to allocate resources effectively.
Phase 4: Response and resolution
Critical resolution actions include containment, eradication, and recovery. Containment limits the incident’s spread and impact, while eradication removes the root cause. Recovery focuses on restoring affected systems and services to normal operations. Strict adherence to predefined protocols and clear collaboration among incident response team members is crucial to ensure swift, thorough resolution. Activities include:
- Implement short- and long-term containment measures to prevent further damage.
- Identify and eliminate the root cause of the incident.
- Restore affected systems and data from clean backups.
- Verify that systems are functioning correctly.
Phase 5: Closure
Document the incident details, actions taken, and lessons learned. By conducting a post-incident review, you can identify what went well and what areas need improvement. Use the information to improve your organization’s incident response capabilities for the future. Closure activities include:
- Compile a detailed incident report.
- Conduct a post-incident review to discuss lessons learned.
- Update response plans and procedures based on insights gained.
Benefits of the incident response phases
As part of an ITOps team, you know the critical role of incident response. In particular, the advantages of following a solid incident response strategy support your ability to:
Maintain service quality
- Readiness: Strong preparation involves developing detailed response plans, training your team, and acquiring the necessary tools. With these in place, teams can respond swiftly and effectively to preserve service quality.
- Identification: Advanced monitoring tools support the early detection of anomalies so you can take immediate action. Taking a proactive stance prevents minor issues from escalating.
Enhance efficiency
- Prioritization: Categorizing and ranking incidents based on severity makes it easy to agree on the most critical issues. From there, you can mobilize resources and expertise to address the situation in an efficient, focused way.
- Incident response: Reduce chaos and downtime with a well-defined process that includes containment, eradication, and recovery. Help your team restore services quickly to reduce an incident’s overall impact.
Minimize downtime
- Containment: Effective response plans include swift containment measures to limit the spread of an incident, plus follow-through to eradicate the root cause. These actions are crucial to minimize downtime and prevent recurrence.
- Recovery: Restore systems and services quickly and securely. Minimize the time services are unavailable to maintain business continuity and routine operations.
Improve continuously
- Refinement: Post-incident reviews enable you to refine your response strategies. Use data and feedback to enhance your team’s readiness and efficacy for similar incidents.
- Adjustment: Use regular updates to adjust your response strategies to address new threats and technologies.
- Enhancement: Use continuous evaluation to refine detection, processes, and team skills to support organizational resilience.
Best practices for effective incident response
Establish clear documentation and communication
Effective response relies heavily on collaboration. Document all incident-related information, including incident details, actions taken, and decisions made. Documentation serves multiple purposes. It provides a record for post-incident analysis, helps knowledge transfer, and makes the response process more transparent.
Use centralized communication channels to inform team members and stakeholders about incident status, response actions, and next steps. This approach minimizes confusion and ensures a coordinated response.
Use automation and ITSM tools
Automation and ITSM tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and efficacy of your incident response phases and framework. Automate repetitive tasks such as initial incident triage, alert notifications, and preliminary containment actions so you can reduce response time and give your team more time to focus on more complex tasks.
Provide a unified ITSM platform to track incidents, manage workflows, and confirm teams follow all incident response steps correctly. ITSM tools facilitate seamless collaboration and documentation to improve response.
Provide regular training and updates
Make sure response teams are well-versed in the latest activities, tools, and best practices. Conduct regular training sessions, simulations, and drills to help people keep their skills sharp as well as learn new procedures and technologies.
Keep plans and playbooks up-to-date with the latest trends and lessons learned from past incidents.
Monitor, review, repeat
Identifying issues before they become significant incidents requires continuous monitoring and regular review. Comprehensive real-time network monitoring, log analysis, and anomaly detection systems can detect anomalies and potential incidents early.
It’s not just about the incidents. Review and analyze monitoring data regularly to uncover patterns, trends, and opportunities for improvement. Integrate feedback into your incident response strategy to ensure your processes remain effective and resilient.
Streamline incident response phases
Automate and accelerate workflows and processes to smooth incident response and reduce the time needed for investigation and resolution. Workflow automation can help you triage alerts and quickly mobilize responders using automated notifications and ticketing.
Seamlessly integrating with ITSM solutions like ServiceNow, BigPanda supports efficient bidirectional ticket creation and updates. Automating notifications ensures that incidents are promptly directed to the appropriate team members. Additionally, BigPanda integrates with third-party automation tools to execute runbook automation and recommend the next steps to streamline incident response.
Get started with BigPanda to automate incident remediation.